The process
Notre processus industriel est l'étape centrale au coeur d'une boucle d'économie circulaire, écologiquement vertueuse, dans laquelle les emballages sont recyclés localement à plus de 80%
RAW MATERIAL SUPPLY PHASE
GEMDOUBS recycles recovered paper and cardboard, coming from:
- 30% of household packaging recovered by communities (mainly Greater Region);
- 70% of product packaging collected from mass distribution (agri-food, etc.) and industry. The raw material is delivered in the form of compressed bales, each weighing between approximately 300 and 1500 kg, which are stored in the bale yard.
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |

LOADING PHASE
The bales are transported by forklift operators to the elevator belt, which lifts them into the pulper tank, where they are defibrated.
 |
|---|
 |

CRUSHING PHASE
In the first step of the crushing process, the husks are crushed with water by the pulper rotor. The paper is thus defibrated, the paper fiber (cellulose) is separated from a majority of the waste - plastics, metals, sludge, etc.
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |

PURIFICATION PHASE
Scrubbers continue this work in more depth by targeting different types of impurities.
The cleaners complete the treatment phase by definitively separating the plastics, staples and glues, leaving only the cellulose fibers used in the manufacture of paper. We thus obtain paper pulp.
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |

TRAINING PHASE
The papermaking process begins. The paper pulp, composed of water and fibers, is projected onto the forming cloth, a sort of conveyor belt through which the water is sucked in, leaving the fibers to make up the still very wet paper.
A continuous sheet of paper is thus formed, according to a certain width (or "width") and a certain thickness (determining the weight).
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |

DRYING PHASE
The still very soft and damp paper then passes through roller presses, in order to mechanically remove as much water as possible.
It is then necessary to complete the drying by calorific means: The strip of paper then circulates around the circumference of approximately 50 large diameter drying cylinders, brought to 130°C by means of circulation of water vapor.
In order to obtain less "blotting" and more solid paper, starch is deposited before the last drying cylinders by roller equipment called "size-press".
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |
FINISHING PHASE
The finally dry strip of paper is wound on a metal mandrel at the end of the line to form a mother reel. The characteristics of the paper are measured and monitored continuously by a scanner located just before this step.
 |
|---|
 |
 |

CONDITIONING PHASE
Second winding phase: the mother bobbin is transferred to the winding machine. The paper is unrolled and rolled up again, this time on cardboard cores, to form several daughter reels, closed with adhesive and labeled.
The reels of PPO (Corrugated Paper) thus obtained have a width of up to approximately 3.35 m.
The mother coil can constitute 2 to 3 daughter coils in the direction of winding.
In the width direction, several daughter reels of smaller complementary "widths" can be cut.
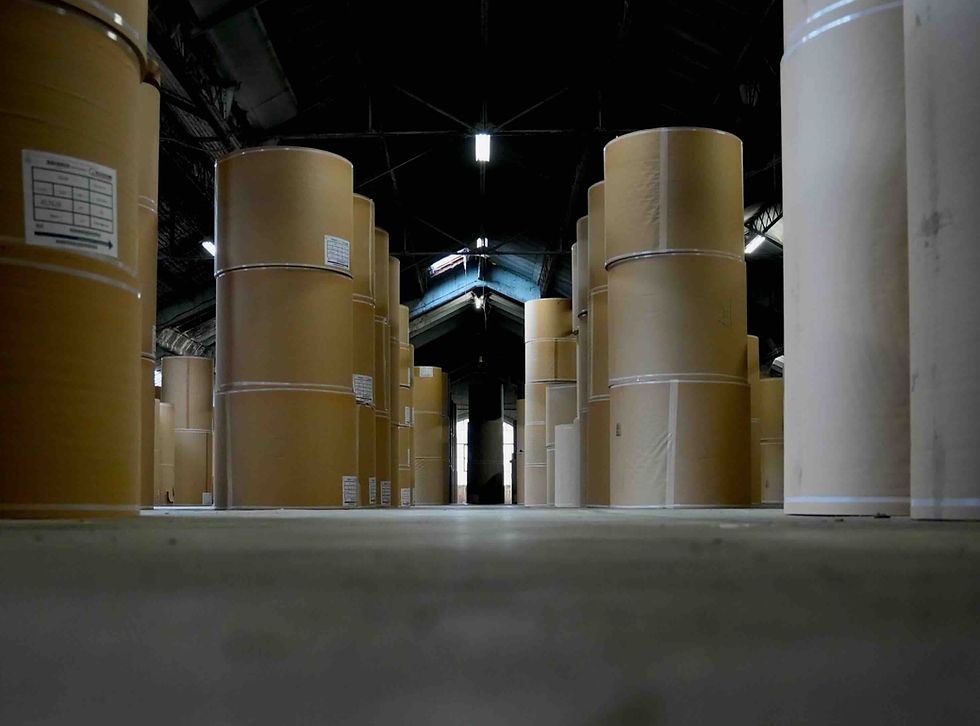
These reels are then transferred to the finished products warehouse and stored vertically, before being shipped to customers.
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
SUMMARY


